


What is EVPN-VXLAN?
EVPN VXLAN Explained
EVPN-VXLAN refers to a network fabric that extends layer 2 connectivity as a network overlay over an existing physical network. It is an open standards technology that creates more agile, secure, and scalable networks in campuses and data centers. EVPN-VXLAN consists of:
- Ethernet VPN (EVPN) which is used as the overlay control plane and provides virtual connectivity between different layer 2/3 domains over an IP or MPLS network.
- Virtual extensible LANs (VXLAN), a common network virtualization overlay protocol that expands the layer 2 network address space from 4,000 to 16 million.



How EVPN-VXLAN works
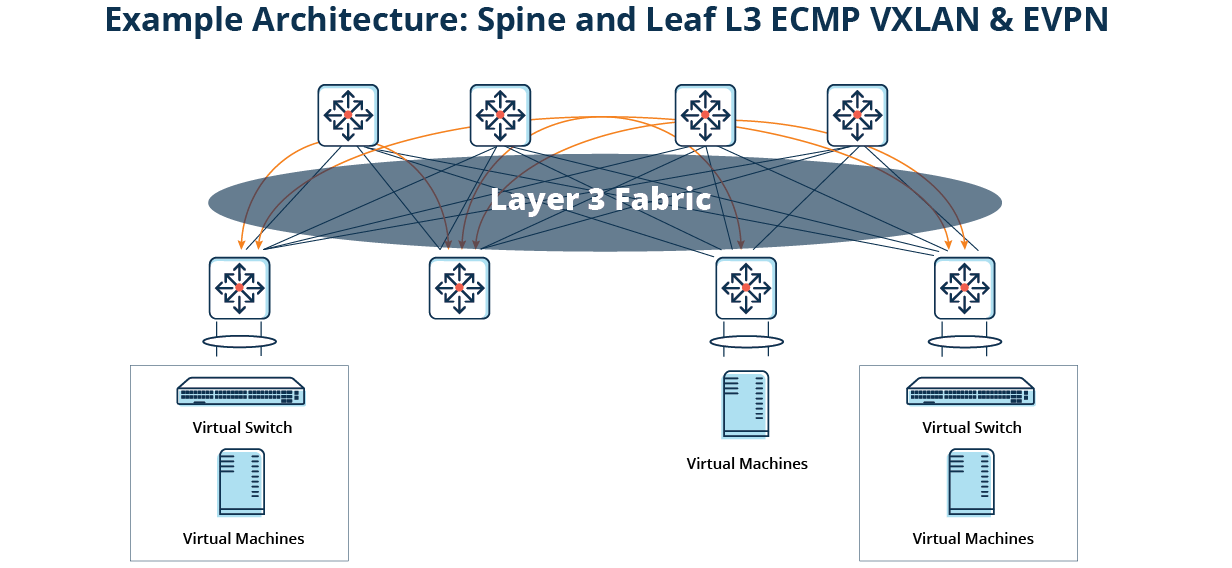
EVPN-VXLAN enables businesses to connect geographically dispersed locations using layer 2 virtual bridging. EVPN-VXLAN provides the scale required by cloud service providers and is often the preferred technology for data center interconnections.
EVPN, as an overlay, supports multi-tenancy and is highly extensible, often using resources from different data centers to deliver a single service. It can provide layer 2 connectivity over physical infrastructure for devices in a virtual network or enable layer 3 routing.
Because it serves as a MAC address learning control plane for overlay networks, EVPN can support different data plane encapsulation technologies. This flexibility is especially appealing for network fabrics that aren’t strictly based on MPLS.
VXLAN封装层2以太网帧laye之类r 3 UDP packets, meaning virtual layer 2 subnets can span underlying layer 3 networks. A VXLAN network identifier (VNI) is used to segment each layer 2 subnet similarly to traditional VLAN IDs.
A VXLAN tunnel endpoint (VTEP) is a VXLAN-capable device that encapsulates and de-encapsulates packets. In the physical network, a switch typically functions as a layer 2 or layer 3 VXLAN gateway and is considered a hardware VTEP. The virtual network equivalents are known as software VTEPs, which are hosted in hypervisors such as VMware ESXi or vSphere.
The rise of EVPN-VXLAN
EVPN-VXLAN has emerged as a popular networking framework largely due to the limitations of traditional VLAN-based networks.
Within campus environments, the proliferation of endpoints due to BYOD, workplace mobility, and IoT is driving a need for more fine-grained segmentation strategies to separate different profiles of users, devices, and traffic.
It’s a similar story in data centers, where more and more workloads are being deployed to support digital transformation. IT needs to protect and manage workloads on an individual basis while preventing hackers from moving laterally from server to server if a breach occurs.
Building an EVPN-VXLAN fabric with Aruba CX
The Aruba CX Switching Portfolio is designed for the evolving, complex demands of modern campus and data center networks, including EVPN-VXLAN-based fabrics. Based on a distributed, non-blocking architecture, Aruba CX switches deliver true wired speed performance from 1GbE to 100GbE.
Aruba CX switches that support EVPN-VXLAN include:
- Aruba CX 6300: Built-in 10/25GbE uplinks (50GbE DAC) and support for up to 10-member stacking
- Aruba CX 6400: A modular 5- or 10-slot switch with up to 28Tbps capacity
- Aruba CX 8325: A 1U switch with 1/10/25/40/100GbE connectivity ideal for leaf or spine switches
- Aruba CX 8360: High-performance 1/10/25/40/100GbE connectivity in a compact 1U form factor
- Aruba CX 8400: 8-slot modular switch with up to 19.2Tbps capacity ideal for campus core
- (Static VXLAN supported onCX 6200.)
All Aruba CX switches are powered byAOS-CX, a cloud-native operating system that simplifies management of EVPN-VXLAN fabrics with:
- Turnkey automation to accelerate built-outs and ongoing network-wide changes.
- Distributed analytics to proactively detect and troubleshoot issues.
- Always-on infrastructure designed for resiliency and zero downtime, even during upgrades.

The Advantages of EVPN-VXLAN
Enterprises using EVPN-VXLAN gain the following benefits:
Flexibility:EVPN-VXLAN supports multiple protocols and shares common architectural elements with other common network services like VPNs, making it easy to integrate into existing networks.
Greater scalability:An EVPN-VXLAN-based architecture enables enterprises to easily add new switches without requiring any redesigns of the underlay network.
Enhanced security:细分割使得它限制交通flows between every connected element in the network, hardening security postures and limiting the blast radius of attacks.
Better performance and resiliency:Latency between network devices is more predictable, especially in spine-leaf architectures, and failure of a single spine or leaf doesn’t have as large an impact on overall fabric performance.





